Total Rainfall#
Setup#
First, we need to import all the necessary libraries. Some of them are specifically developed to handle the download and plotting of the data and are hosted at the indicators set-up repository in GitHub
Show code cell source
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
import os
import os.path as op
import sys
import folium
from myst_nb import glue
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
sys.path.append("../../../../indicators_setup")
from ind_setup.plotting_int import plot_timeseries_interactive
from ind_setup.plotting import plot_bar_probs
from ind_setup.colors import get_df_col
from ind_setup.core import fontsize
from ind_setup.tables import plot_df_table, table_rain_a_summary
sys.path.append("../../../functions")
from data_downloaders import GHCN
from data_downloaders import GHCN, download_oni_index
from ind_setup.plotting_int import plot_oni_index_th
from ind_setup.plotting import plot_bar_probs_ONI, add_oni_cat
import df2img
country = 'Palau'
vars_interest = ['PRCP']
Get Data#
update_data = False
path_data = "../../../data"
path_figs = "../../../matrix_cc/figures"
Show code cell source
if update_data:
df_country = GHCN.get_country_code(country)
print(f'The GHCN code for {country} is {df_country["Code"].values[0]}')
df_stations = GHCN.download_stations_info()
df_country_stations = df_stations[df_stations['ID'].str.startswith(df_country.Code.values[0])]
print(f'There are {df_country_stations.shape[0]} stations in {country}')
Obervations from Koror Station#
https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/data/global-historical-climatology-network-daily/doc/GHCND_documentation.pdf
The data used for this analysis comes from the GHCN (Global Historical Climatology Network)-Daily database.
This a database that addresses the critical need for historical daily temperature, precipitation, and snow records over global land areas. GHCN-Daily is a
composite of climate records from numerous sources that were merged and then subjected to a suite of
quality assurance reviews. The archive includes over 40 meteorological elements including temperature daily maximum/minimum, temperature at observation time,
precipitation and more.
Show code cell source
if update_data:
GHCND_dir = 'https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/data/global-historical-climatology-network-daily/access/'
id = 'PSW00040309' # Koror Station
dict_prcp = GHCN.extract_dict_data_var(GHCND_dir, 'PRCP', df_country_stations.loc[df_country_stations['ID'] == id])[0]
data = dict_prcp[0]['data']#.dropna()
data.to_pickle(op.join(path_data, 'GHCN_precipitation.pkl'))
else:
data = pd.read_pickle(op.join(path_data, 'GHCN_precipitation.pkl'))
Analysis#
dict_prcp = [{'data' : data, 'var' : 'PRCP', 'ax' : 1, 'label' : 'Precipitation'}, ]
Plotting#
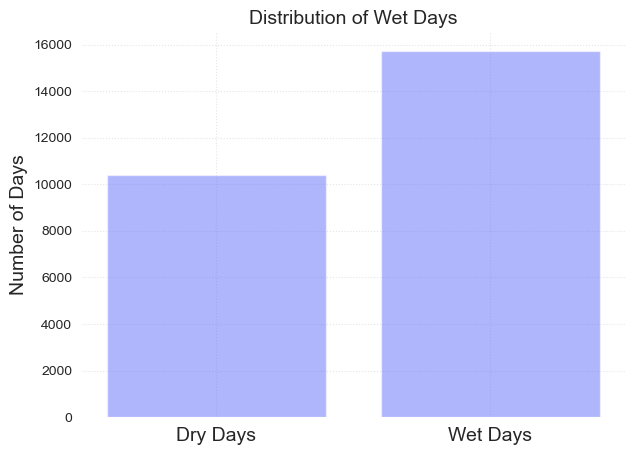
Wet days#
Wet days are considered when rainfall is above 1mm
data = dict_prcp[0]['data']#.dropna()
data = data.groupby(data.index.year).filter(lambda x: len(x) >= 300).dropna()
glue("n_years", len(np.unique(data.index.year)), display=False)
data['wet_day'] = np.where(data['PRCP'] > 1, 1, np.where((np.isnan(data['PRCP'])==True), np.nan, 0))
fig, ax = plot_bar_probs(x = [0, 1], y = data.groupby('wet_day').count()['PRCP'].values, labels = ['Dry Days', 'Wet Days'])
ax.set_title('Distribution of Wet Days', fontsize = fontsize)
ax.set_ylabel('Number of Days', fontsize = fontsize)
Text(0, 0.5, 'Number of Days')
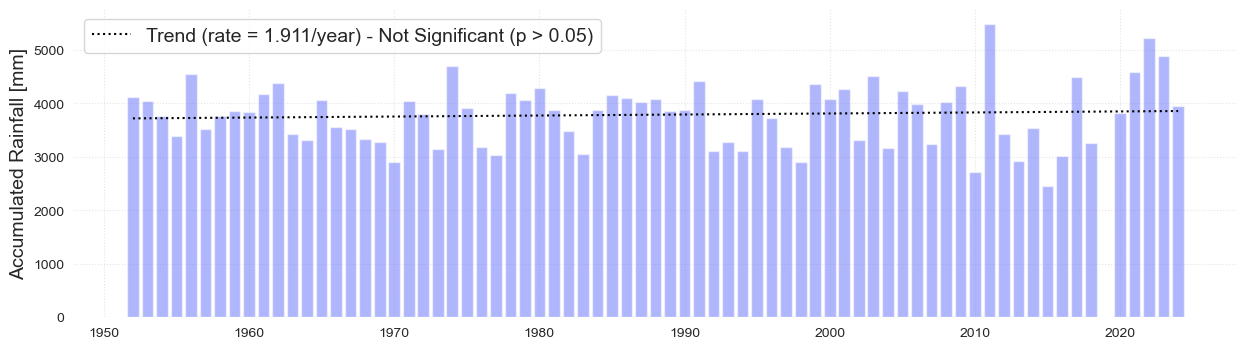
Accumulated precipitation#
The following plot analyzes the accumulated precipitation for each year since 1951.
# Correct accumulated precipitation with number of observations per year to make fair comparisons and trends
datag = (data.groupby(data.index.year).sum()/ data.groupby(data.index.year).count()) * 365
datag.index = pd.to_datetime(datag.index, format = '%Y')
dict_plot = [{'data' : datag, 'var' : 'PRCP', 'ax' : 1, 'label':'Accumulated precipitation [mm]'},]
fig, ax = plot_bar_probs(x = datag.index.year, y = datag['PRCP'].values,
trendline = True, figsize = [15, 4])
ax.set_ylabel('Accumulated Rainfall [mm]', fontsize = fontsize)
glue("accum_rain", fig, display=False)

Number of days over and above 1mm threshold#
The following plot analyzes the number of wet (over 1mm) and dry days over time
threshold = 1 #np.percentile(data['PRCP'].dropna(), 90)
data['wet_day_t'] = np.where(data['PRCP'] > threshold, 1, np.where((np.isnan(data['PRCP'])==True), np.nan, 0))
data_th = data.groupby([data.index.year, data.wet_day_t]).count()['PRCP']
data_th = data_th/data.groupby(data.index.year).count()['PRCP'] * 365
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize = [15, 5])
data_th.unstack().plot(kind = 'bar', stacked = True, ax = ax, color = get_df_col()[:2], edgecolor = 'white', alpha = .5)
ax.set_ylabel('Number of days', fontsize = fontsize)
Text(0, 0.5, 'Number of days')
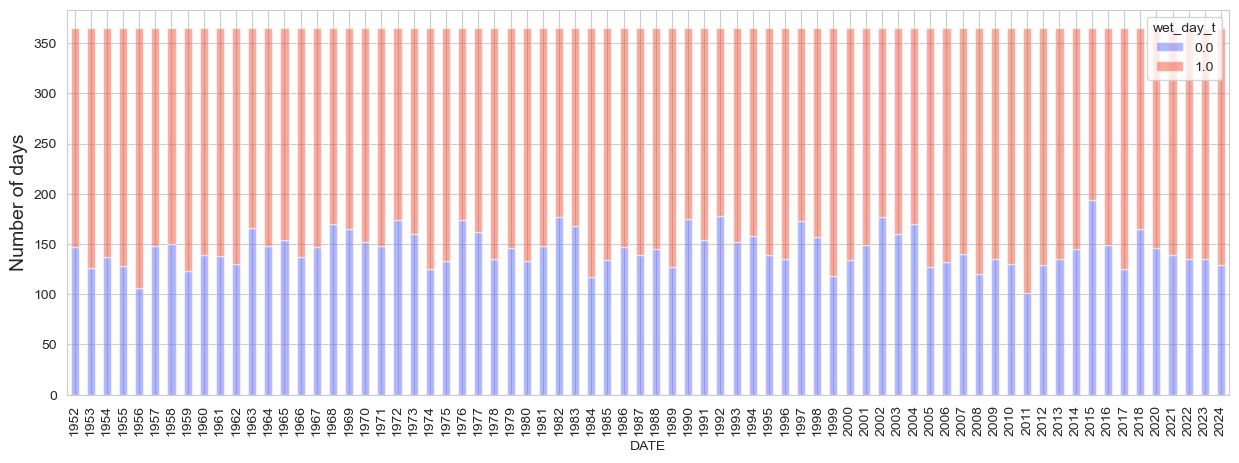
The following plots analyze independently the number of wet and dry days over time as well the trend over time which is not significant in both cases.
#Wet days
data2 = data.loc[data['wet_day_t'] == 1]
data2 = data2.groupby(data2.index.year).count()
fig, ax, trend = plot_bar_probs(x = data2.index, y = data2.PRCP.values, trendline = True,
y_label = 'Number of wet days [>1mm]', figsize = [15, 4], return_trend = True)
plt.savefig(op.join(path_figs, 'F7a_Wet_days_1mm.png'), dpi=300, bbox_inches='tight')
glue("trend_wet", float(trend), display=False)
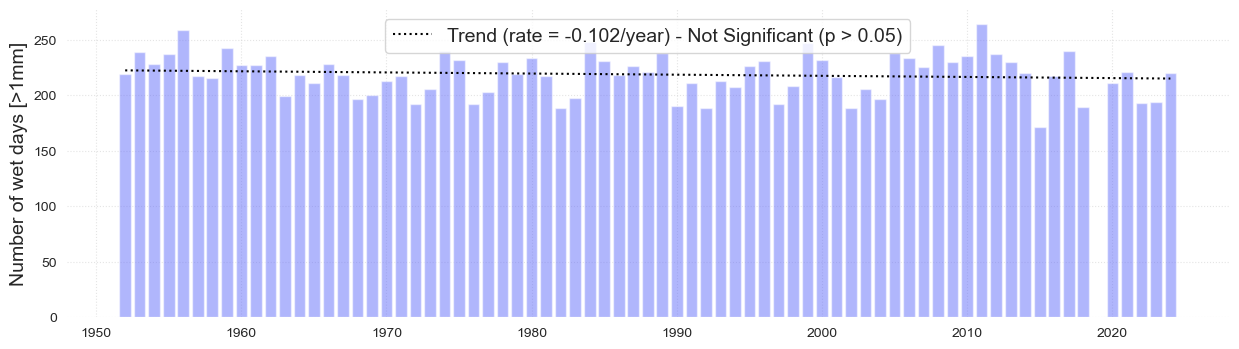
Dry days#
data2 = data.loc[data['wet_day_t'] == 0]
data2 = data2.groupby(data2.index.year).count()
fig, ax, trend = plot_bar_probs(x = data2.index, y = data2.PRCP.values, trendline = True,
y_label = 'Number of dry days [<1mm]', figsize = [15, 4], return_trend = True)
plt.savefig(op.join(path_figs, 'F6a_Number_dry.png'), dpi=300, bbox_inches='tight')
glue('trend_dry', float(trend), display=False)
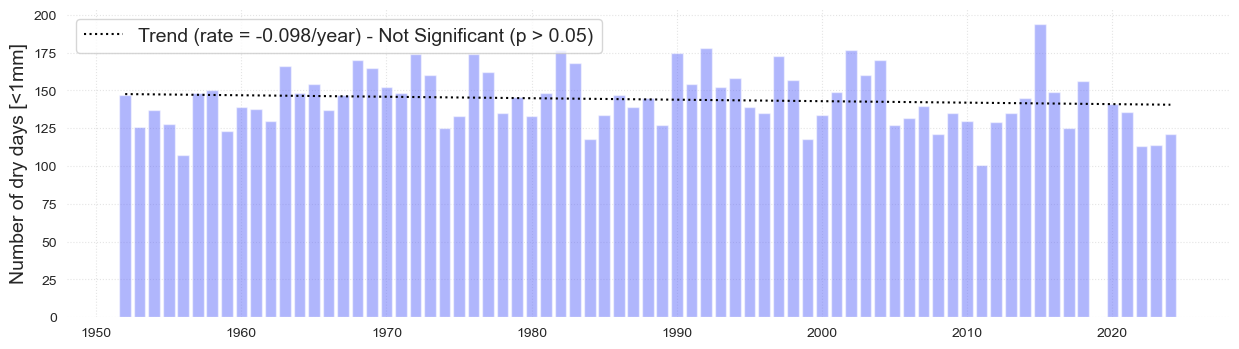
Annual maxima#
The evolution of the annual maximum precipitation is shown in the following plot.
data_max = data.groupby(data.index.year).max()
data_max.index = pd.to_datetime(data_max.index, format = '%Y')
dict_plot = [{'data' : data_max, 'var' : 'PRCP', 'ax' : 1, 'label':'Annual daily maxima'},]
plot_timeseries_interactive(dict_plot, trendline = True, figsize = (25, 12), label_yaxes = 'Precipitation [mm]');
Table#
Table sumarizing different metrics of the data analyzed in the plots above
df = table_rain_a_summary(data)
fig = plot_df_table(df.T, figsize = (600, 350),)
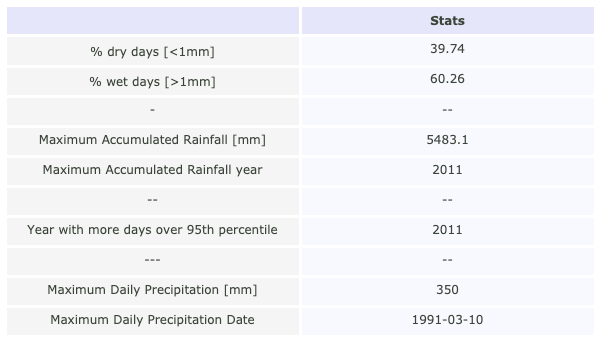
ONI index#
The Oceanic Niño Index (ONI) is the standard measure used to monitor El Niño and La Niña events. It is based on sea surface temperature anomalies in the central equatorial Pacific (Niño 3.4 region) averaged over 3-month periods.
https://origin.cpc.ncep.noaa.gov/products/analysis_monitoring/ensostuff/ONI_v5.php
p_data = 'https://psl.noaa.gov/data/correlation/oni.data'
if update_data:
df1 = download_oni_index(p_data)
df1.to_pickle(op.join(path_data, 'oni_index.pkl'))
else:
df1 = pd.read_pickle(op.join(path_data, 'oni_index.pkl'))
lims = [-.5, .5]
plot_oni_index_th(df1, lims = lims)
Analysis#
st_data = data
st_data_monthly = st_data.resample('M').mean()
st_data_monthly.index = pd.DatetimeIndex(st_data_monthly.index).to_period('M').to_timestamp() + pd.offsets.MonthBegin(1)
df1['prcp'] = st_data_monthly['PRCP']#.rolling(window=rolling_mean).mean()
df1 = add_oni_cat(df1, lims = lims)
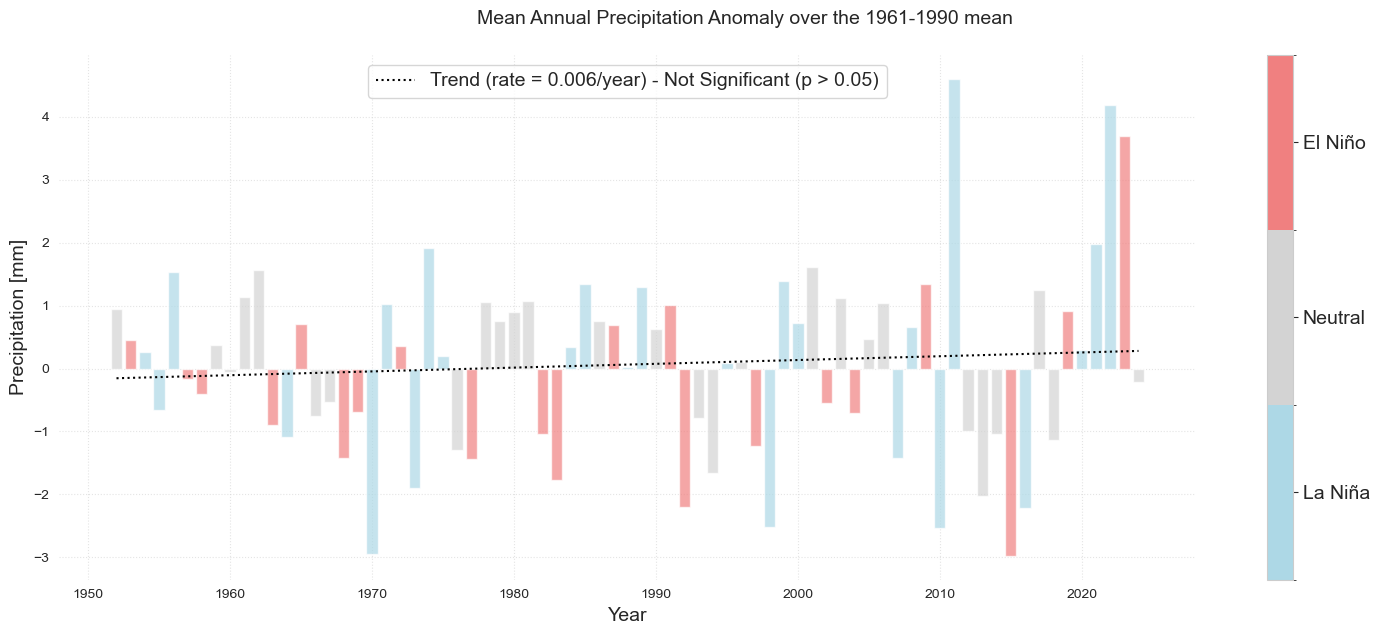
Plotting#
df2 = df1.resample('Y').mean()
df2['prcp_ref'] = df2.prcp - df2.loc['1961':'1990'].prcp.mean()
fig = plot_bar_probs_ONI(df2, var='prcp_ref', y_label = 'Precipitation [mm]')
fig.suptitle('Mean Annual Precipitation Anomaly over the 1961-1990 mean', fontsize = fontsize, y = 1.05)
plt.savefig(op.join(path_figs, 'F5_Rain_mean.png'), dpi=300, bbox_inches='tight')
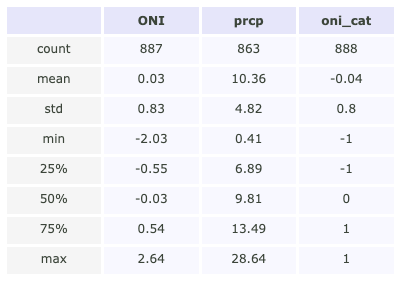
df_format = np.round(df1.describe(), 2)
Table#
Table sumarizing different metrics of the data analyzed in the plots above
fig = plot_df_table(df_format, figsize = (400, 300))
df2img.save_dataframe(fig=fig, filename="getting_started.png")